Carbon Dioxide
Atmospheric Carbon Dioxid monthly, Mauna Loa, Hawaii
The CO2 data (red curve), measured in Mauna Loa as the mole fraction in dry air, constitutes the largest register of direct CO2 measurements in the atmosphere. They were initiated by C. David Keeling of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in March 1958 at a facility of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration [Keeling, 1976].
The month graph, updated daily, shows as individual points daily and hourly mean CO2 for the last 31 days. Daily average CO2 values are computed from selected hourly values that satisfy 'background' conditions, i.e. stability and persistence of CO2 concentrations (read below for more information). That means the daily averages shown on the plot are likely computed from a subset of the hourly averages. It also is possible that no daily average can be computed even though hourly averages exist, because all of the hourly averages for a day do not satisfy the background conditions. These daily average values may also change as a result of the selection process as additional data become available. The daily means are based on hours during which CO2 was likely representative of “background” conditions, defined as times when the measurement is representative of air at mid-altitudes over the Pacific Ocean.
The year graph is updated weekly, shows as individual points daily mean CO2 up to and including the week (Sunday through Saturday) previous to today. The daily means are based on hours during which CO2 was likely representative of “background” conditions, defined as times when the measurement is representative of air at mid-altitudes over the Pacific Ocean.
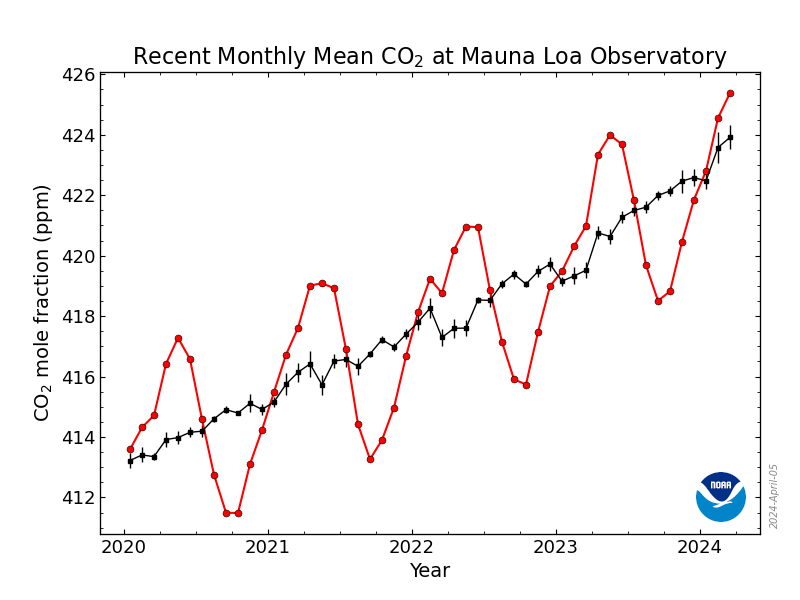
The 5 year graph shows recent monthly mean carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii.

